Type 2 diabetes often develops silently, but catching the warning signs early can help prevent serious complications. Here are 13 symptoms that could indicate high blood sugar:
1. Frequent Urination (Polyuria)
Waking up multiple times at night to pee? Your kidneys might be working overtime to flush out excess glucose.
2. Constant Thirst (Polydipsia)
If you’re always thirsty, it’s likely because your body is losing too much fluid through frequent urination.
3. Uncontrollable Hunger (Polyphagia)
Blood sugar swings can trick your body into thinking it’s starving, causing intense cravings.
4. Dry Mouth
A lack of saliva can lead to discomfort, bad breath, and a higher risk of gum disease.
5. Unexplained Weight Loss or Gain
Losing weight fast (10–20 lbs in a few months) without trying? Your body may be breaking down muscle for energy. On the flip side, cravings for sugary foods can lead to weight gain.
6. Fatigue & Irritability
Feeling drained all the time? Poor glucose absorption and interrupted sleep (from frequent urination) can leave you exhausted and moody.
7. Blurry Vision
High blood sugar can alter the shape of your eye lens, leading to blurred vision. If untreated, it may cause permanent damage.

8. Persistent Headaches
Headaches can be an early sign of high blood sugar and may worsen as levels spike.
9. Slow-Healing Cuts & Bruises
Too much sugar in your bloodstream damages blood vessels, slowing down the healing process.
10. Frequent Yeast Infections
Sugar feeds bacteria and fungi, making infections like vaginal yeast overgrowth more common.
11. Numbness & Tingling in Hands & Feet
Diabetes-related nerve damage (neuropathy) can cause burning, tingling, or numbness in your extremities.
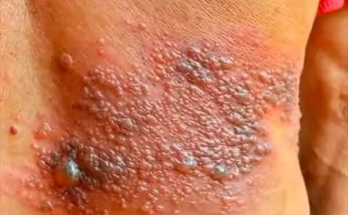
12. Dark Patches on Skin
Velvety dark skin on the neck, armpits, or groin (acanthosis nigricans) can be a sign of insulin resistance.
13. Sexual Dysfunction
Diabetes damages blood vessels and nerves, leading to issues like vaginal dryness in women and erectile dysfunction in men (affecting 35–75% of diabetic men).
Think you might have diabetes? See your doctor for a blood test—early action can make all the difference.