Here’s a revised version that maintains the key information while improving clarity and flow:
The Spotted Lanternfly: What You Need to Know
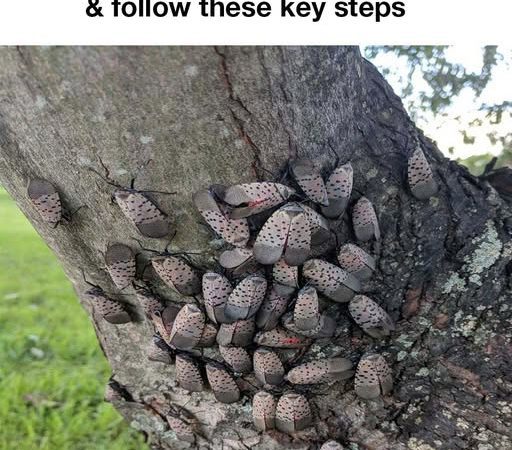
A colorful but destructive pest has been causing growing concern across multiple U.S. states. The spotted lanternfly (Lycorma delicatula), while visually striking, poses serious threats to agriculture and local ecosystems. First detected in Pennsylvania in 2014, this invasive species has since spread to several neighboring states.
Identification:
Adult lanternflies measure about 1 inch long with distinctive wings – gray forewings with black spots and bright red hindwings with black and white markings. Younger nymphs appear black with white spots, turning red as they mature.
Why Control Matters:
These pests feed on over 70 plant species, including valuable crops like grapes and apples. Their feeding weakens plants and leaves behind a sticky residue called honeydew that promotes mold growth. This combination threatens both agricultural productivity and residential areas.
Management Methods:
- Physical Removal:
- Crush individual insects (wear gloves if sensitive to residues)
- Scrape egg masses into alcohol-based solutions
- Trapping:
- Use sticky bands on trees (with protective mesh to safeguard other wildlife)
- Chemical Options:
- Consider insecticidal soaps or neem oil for targeted treatment
- Always follow product instructions carefully
- Reporting:
- Contact local agricultural authorities to report sightings
- Follow regional guidelines for control measures
By staying informed and taking appropriate action, we can all help protect our local environments and agricultural resources from this invasive species.
Source: cooktopcove.com